Design Model
Copyright © 2003
2003-11-03
| Revision History | |
|---|---|
| Revision 0.1 | 2003-05-19 |
| Initial public release. | |
| Revision 0.2 | 2003-06-09 |
| Corrected some cardinalities, extended descriptions, added operations. | |
| Revision 0.3 | 2003-06-15 |
| Added "user logs in" sequence diagram. | |
| Revision 0.4 | 2003-06-23 |
| Extended from static model to analysis model. | |
| Revision 0.5 | 2003-10-06 |
| Incorporated optional feature "Resource Reservation" (see appendix of this document for the use cases derived from that feature); refined package structure; introduced distinction between physical resource containment hierarchy and resource usage. | |
| Revision 0.6 | 2003-10-20 |
| Extended from analysis model to design model. | |
| Revision 0.7 | 2003-11-03 |
| Refined model for server and client; added sequence diagrams for verification. | |
Abstract
This document contains the class diagrams and class descriptions that resulted from the static analysis and the design analysis as well as sequence diagrams and state chart diagrams that we used to verify the class model.
Table of Contents
- 1. Overview
- 2. Package: model
- 2.1. Package: model.entity
- 2.1.1. Class: EntityType
- 2.1.2. Class: EntityTypeID
- 2.1.3. Class: ResourceType
- 2.1.4. Class: EmployeeType
- 2.1.5. Class: Entity
- 2.1.6. Class: EntityID
- 2.1.7. Class: Resource
- 2.1.8. Class: Employee
- 2.1.9. Class: AttributeType
- 2.1.10. Class: BooleanAttributeType
- 2.1.11. Class: NumberAttributeType
- 2.1.12. Class: TextAttributeType
- 2.1.13. Class: Attribute
- 2.1.14. Class: BooleanAttribute
- 2.1.15. Class: NumberAttribute
- 2.1.16. Class: TextAttribute
- 2.2. Package: model.linkage
- 2.3. Package: model.user
- 2.4. Package: model.filter
- 3. Package: client
- 4. Package: server
- 5. Appendix: .NET Event Handling
- 6. Appendix: Use Cases
So far, the design model only covers a subset of all use cases - completely defined in the document “Use Cases”. The remaining use cases will be considered during the next revisions of this document. The use cases covered so far are:
User logs in
Create filtered collection of resource entries
Edit resources
This document is organized along the package structure of the MRMS. Every package describes one aspect of the system:
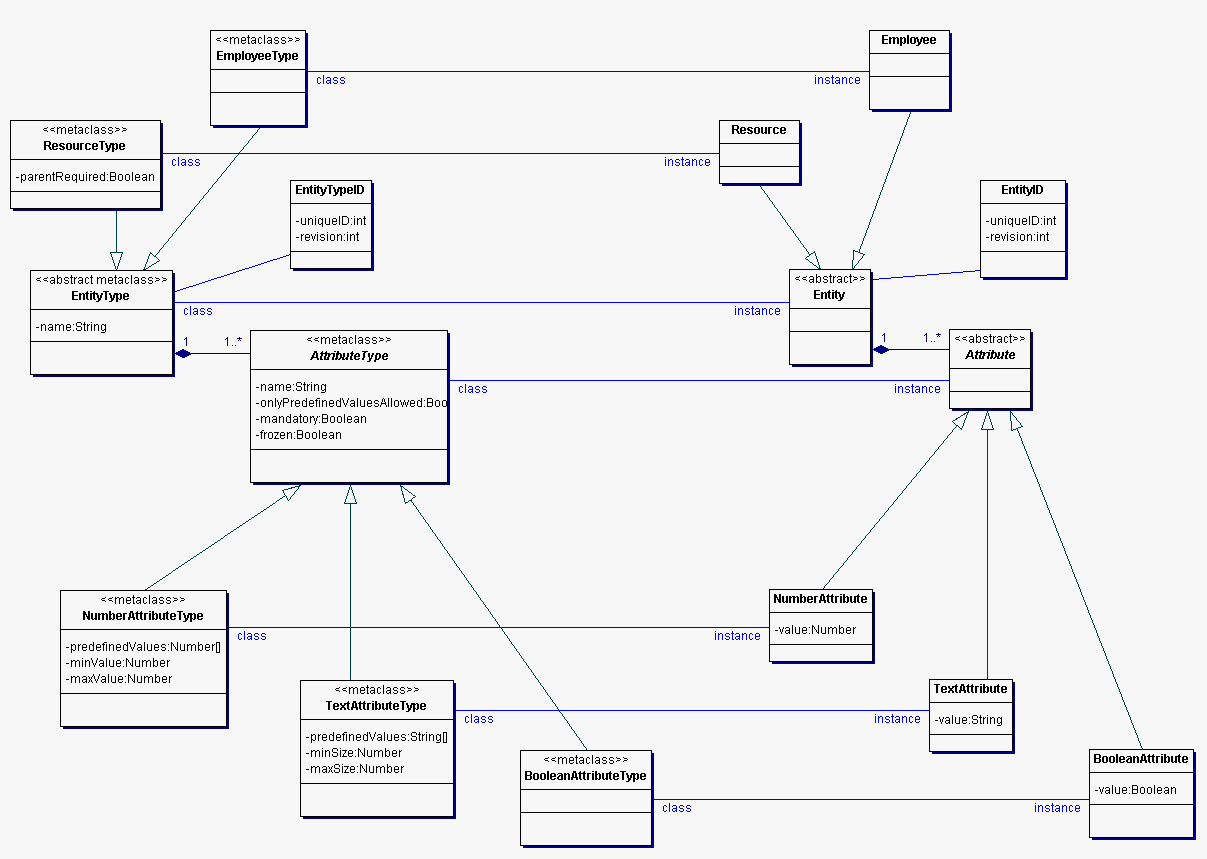
model.entity: The MRMS can handle resources and the employees; the attributes that are to be saved for each resource type and employee type can be configured by an administrator. This common functionality is pulled up to the super type Entity. The package model.entity contains the classes to handle entities (resources, employees) and their attributes (number, text, boolean).
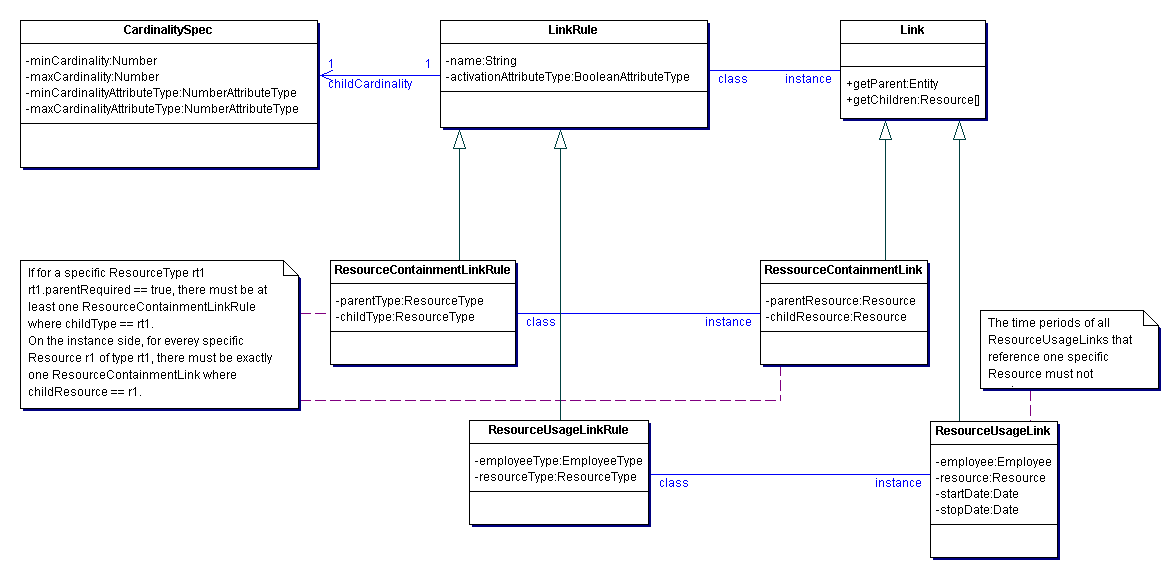
model.linkage: Resources and employees do not exist detached. Resources can be organized in a physical containment structure (e.g. a room contains workplaces, workplaces contain a computer, and so on) and resources can be used by employees. The package model.linkage contains the classes that are necessary to represent these links.
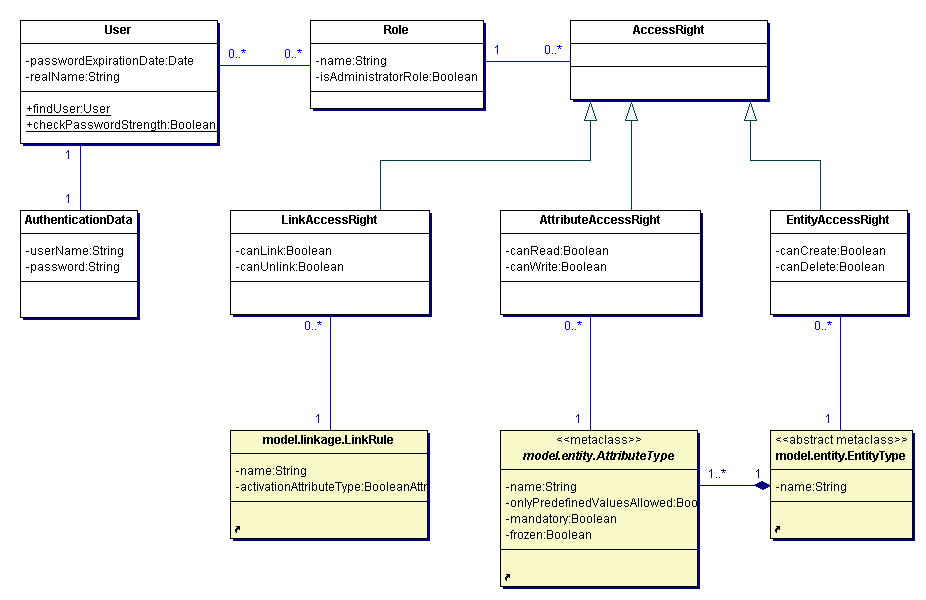
model.user: The users of the system need different access rights according to the role they play in the business. The package model.user contains the classes that represent the rights users have to create and delete entities, edit their attributes and create links.
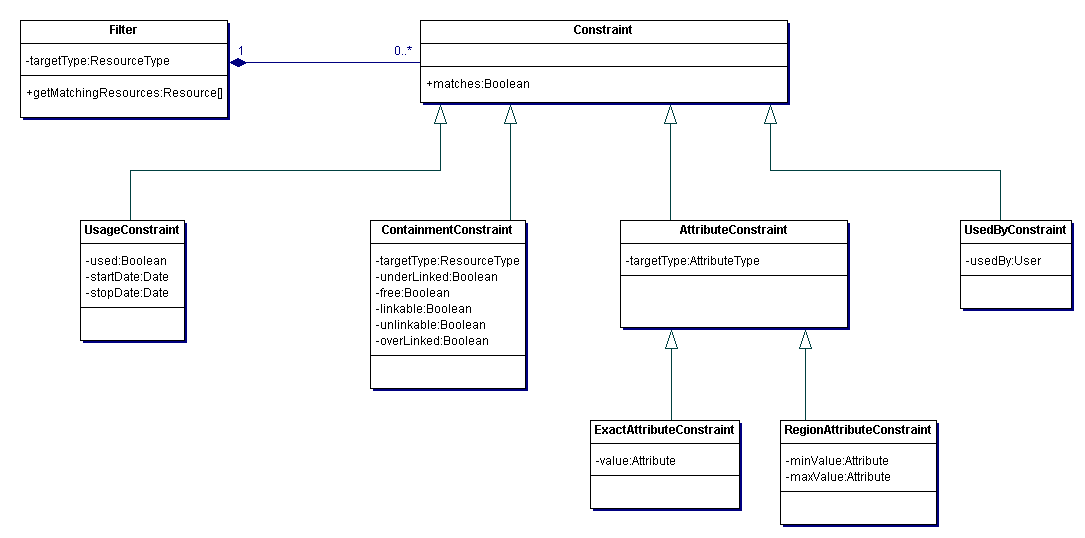
model.filter: Creating a filtered collection of resources is a complex function that is required in different use cases. The package model.filter contains the classes needed to configure a filter with constraints and execute it.
client: Classes needed to realize an interaction between the user and the MRMS.
server: Classes for the MRMS server.
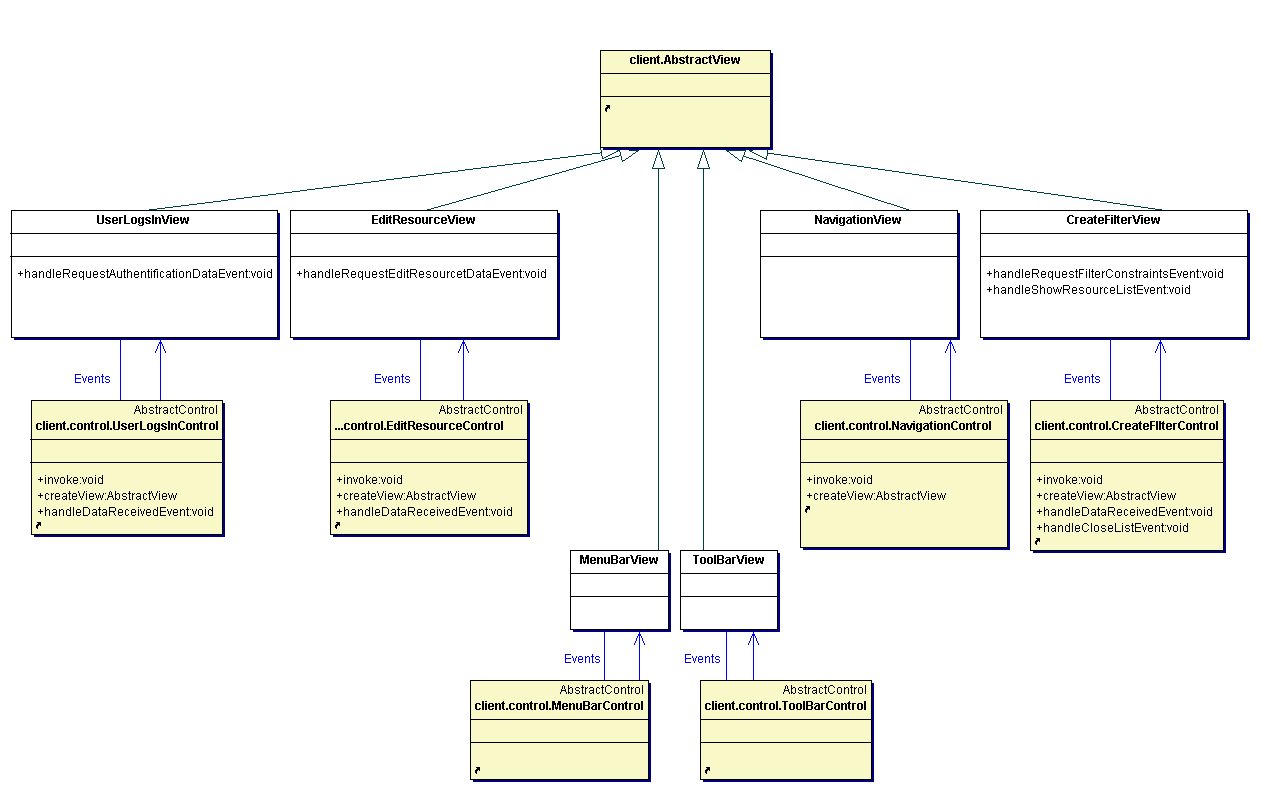
(The classes imported from others packages are colored yellow.)
This package does not contain any classes but only the subpackages entity, linkage, user and filter.
The following diagram depicts the classes to handle entities (resources, employees) and their attributes (number, text, boolean).
- Description
An EntityType has a name and specifies (by composition) the Attributes that an Entity of this type has, it references a unique EntityTypeID.
- Attributes
name (String): the name of the EntityType
- Operations
---
- Description
An EntityTypeID is a unique identifier for an EntityType.
- Attributes
uniqueID (int): an integer which is unique within the set of all EntityTypes
revision (int): an integer which is incremented by the server with every change; this field is used by the server to verify that the EntityType a client refers to has not changed since the client received the EntityType's data
- Operations
---
- Description
A ResourceType is a specialised EntityType for defining Resources.
- Attributes
parentRequired (Boolean): specifies whether instances of this ResourceType must have a parent Resource
- Operations
---
- Description
An EmployeeType is a specialised EntityType for defining Employees.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
---
- Description
An Entity is composed of its Attributes and is an instance of an EntityType which specifies which Attributes the Entity may have, it references a unique EntityID.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
---
- Description
An EntityID is a unique identifier for an Entity.
- Attributes
uniqueID (int): an integer which is unique within the set of all Entitys
revision (int): an integer which is incremented by the server with every change; this field is used by the server to verify that the Entity a client refers to has not changed since the client received the Entity's data
- Operations
---
- Description
A Resource is a specialised Entity for representing real-life-resources and is an instance of a ResourceType which specifies if this Resource must have a parent Resource within the Resources-Containment-Hierarchy.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
---
- Description
An Employee is a specialised Entity for representing users of real-life-resources and is an instance of an EmployeeType.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
---
- Description
Abstract base class for attribute types that an EntityType is composed of.
- Attributes
name (String): the name of the AttributeType
onlyPredefinedValuesAllowed (Boolean): if true, the user may only select the predefined values for an Attribute that has this type; if false, he may enter another value as well
mandatory (Boolean): if true, the user must enter a value for Attributes of this type
frozen (Boolean): if true, the user may not change the value of Attributes of this type
- Operations
---
- Description
Concrete AttributeType for logical property characterisation of an Entity.
- Attributes
value (Boolean): logical property characterisation of an Entity
- Operations
---
- Description
Concrete AttributeType for NumericalAttributes.
- Attributes
predefinedValues (Number[]): an array specifying predefined values for Attributes of this type
minValue (Number): the minimum value Attributes of this type may have
maxValue (Number): the maximum value Attributes of this type may have
- Operations
---
- Description
Concrete AttributeType for TextAttributes.
- Attributes
predefinedValues (String[]): an array specifying predefined values for Attributes of this type
minSize (Number): the minimum number of characters Attributes of this type may have
maxSize (Number): the maximum number of characters Attributes of this type may have
- Operations
---
- Description
Abstract base class for Attributes that an Entity is composed of.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
---
- Description
Concrete Attribute for a boolean property characterisation of an Entity.
- Attributes
value (Boolean): numerical property characterisation of an Entity
- Operations
---
- Description
Concrete Attribute for a numerical property characterisation of an Entity.
- Attributes
value (Number): numerical property characterisation of an Entity
- Operations
---
The following diagram depicts the classes that are necessary to represent the physical containment links between resources and resources and the usage links between resources and employees.
- Description
A Link Rule defines the characteristics of a consistent Link. Both the physical containment structure of the resources as well as the usages of the resource by the users can be modelled as links. In both cases the corresponding link rules have the characteristic that the cardinality of one side is 1; for the physical containment links this side is the parent resource type and for the usage links this side is the employee type. The other side of the link rule can have an arbitrary cardinality (i.e. the number of children a parent has in the physical containment structure as well as the number of resources an employee may use is not constrained by the system but can be customized by the administrator); this cardinality is contained in the CardinalitySpec referenced by the LinkRule. A LinkRule can reference an BooleanAttributeType of the parent resource / using employee; in this case Links of this LinkRule can only be created for those Resources / Employees where the corresponding BooleanAttribute is true.
- Attributes
name (String): name of the LinkRule
- Operations
---
- Description
Base class for ResourceContainmentLink and ResourceUsageLink.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
---
- Description
A ResourceContainmentLinkRule defines the characteristics of a consistent ResourceContainmentLink. It references two ResourceTypes which may be linked together by a ResourceContainmentLink.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
---
- Description
A ResourceContainmentLink references two Resources that are linked together by it; one resource takes the parent role, the other is its child in the pysical containment. Its consistency is checked against the ResourceContainment LinkRule references.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
---
- Description
A ResourceUsageLinkRule defines the characteristics of a consistent ResourceUsageLink. It references one ResourceType and one EmployeeType whose instances may be linked together by a ResourceUsageLink.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
---
- Description
A ResourceUsageLink references one Resource and one Employee that are linked together by it. Its consistency is checked against the ResourceUsageLinkRule it references. There may be more than one ResourceUsageLink at a Resource; but only one of can be active at a certain time.
- Attributes
startDate (Date): Time when usage starts.
stopDate (Date): Time when usage expires.
- Operations
---
- Description
Specifies the minimum and maximum cardinality for a certain ResourceType, referenced by a ResourceUsageLinkRule or a ResourceContainmentLinkRule. Example: A ResourceContainmentLinkRule has two ends ResourceType1 (parent) and ResourceType2 (child). The ResourceType1 always has the cardinality 1 while ResourceType2 has the cardinality min=1 and max=4, this means that one specific Resource of ResourceType1 must have at least 1 and may have up to 4 Links to Resources of ResourceType2. The CardinalitySpec may also reference a NumberAttributeType of the ResourceType1.
- Attributes
minCardinality (Number): value for the minimum cardinality; will be ignored when there is a “min”-reference to a NumberAttributeType, in this case the NumberAttribute's value will be used instead
maxCardinality (Number): value for the maximum cardinality; will be ignored when there is a “max”-reference to a NumberAttributeType, in this case the NumberAttribute's value will be used instead
- Operations
---
The following diagram depicts the classes for user and access rights management of the MRMS.
- Description
Value class, encapsulating the authentication data of a user.
- Attributes
userName (String): the user's name
password (String): the user's password
- Operations
---
- Description
Class for user accounts of the MRMS. Its instances may play Roles in the system.
- Attributes
passwordExpirationDate (Date): date after which the user has to enter a new password
realName (String): real name of the user
- Operations
static checkPasswordStrength(password: String): Boolean
- Effect
Checks, if the given password String is strong enough (minimum length, mixed letters and numbers, ...) to be accepted by the system.
- Parameters
password: the password to be checked
- Return
The boolean value true, iff the password is strong enough.
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
Control class of the use case “User changes password”.
static findUser(authData: AuthenticationData): User
- Effect
Searches the system for a User matching the given AuthenticationData.
- Parameters
authData: the AuthenticationData to search for
- Return
If a matching User object could be found it is returned, otherwise the operation returns the null pointer.
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
Control class of the use case “User logs in”.
- Description
A Role defines which AccessRights its players (Users) have.
- Attributes
name (String): name of the Role
isAdministratorRole (Boolean): defines if Users of the Role have administration rights
- Operations
---
- Description
Abstract base class for access rights. If a Role references an AccessRight it has this AccessRight. Users have the AccessRights which the Roles they play have.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
---
- Description
Concrete AccessRight that defines owner's authority of working with Resources that are of a specific ResourceType.
- Attributes
canCreate (Boolean): defines if Resources of the referenced ResourceType may be created
canDelete (Boolena): defines if Resources of the referenced ResourceType may be deleted
- Operations
---
- Description
Concrete AccessRight that defines owner's authority of working with Atrributes of a specific AttributeType that belongs to a specific ResourceType.
- Attributes
canRead (Boolean): defines if Attributes of the referenced AttributeType may be read
canWrite (Boolean): defines if Attributes of the referenced AttributeType may be written
- Operations
---
- Description
Concrete AccessRight that defines owner's authority of creating and deleting Links according to a specific LinkRule.
- Attributes
canLink (Boolean): defines if Links according to the referenced LinkRule may be created
canUnlink (Boolean): defines if Links according to the referenced LinkRule may be deleted
- Operations
---
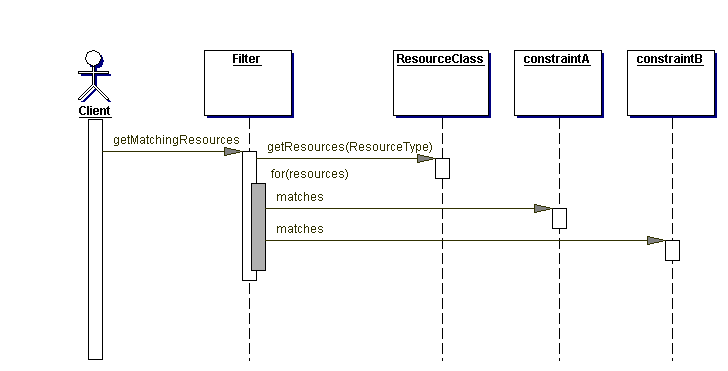
The following diagram depicts the classes needed to configure a filter and get a collection of Resources out of it.
- Description
A Filter is used to get a subset of all Resources of the referenced ResourceType. The Filter is defined by the Constraints it is composed of.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
getMatchingResources(): Resource[]
- Effect
Searches the system for Resources matching the referenced Constraints.
- Parameters
---
- Return
An array of the matching Resources.
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
Control class of the use case “Create filtered collection of resource entries”.
- Description
Abstract base class for constraints. Constraints are used by a Filter to describe a specific state that Resource must fulfill to pass.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
matches(resource: Resource): Boolean
- Effect
Tests, if the given Resource matches this Constraint.
- Parameters
resource: the Resource to be tested
- Return
The boolean value true, iff the given Resource matches this Constraint.
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
Class Filter.
- Description
An AttributeConstraint is a concrete Constraint that checks whether an Attribute of the referenced AttributeType is either equal to the referenced Attribute or lays between the two referenced min- and max-Attributes.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
---
- Description
A ContainmentConstraint is a concrete Constraint that checks whether a Resource matches the physical containment state that is described by the following attributes. A ContainmentConstraint references the LinkRule it refers to. If in this LinkRule the ResourceType that is to be filtered has (1) the parent role minimum and maximum cardinality are taken from LinkRule's CardinalitySpec and refer to the number of children; if it has (2) the client role then min = max = 1 iff the field requiresParent of the ResourceType is true, min = max = 0 otherwise.
- Attributes
underLinked (Boolean): cur < min
free (Boolean): cur = 0
linkable (Boolean): cur < max
unlinkable (Boolean): cur >= max
overLinked (Boolean): cur > max
- Operations
---
- Description
A UsageConstraint is a concrete Constraint that checks whether a Resource is used or unused in a given time period.
- Attributes
used (Boolean): Defines whether the filtered Resources have to be used or unused in the given time period.
startDate (Date): Start time of the time time period.
stopDate (Date): End time of the time period.
- Operations
---
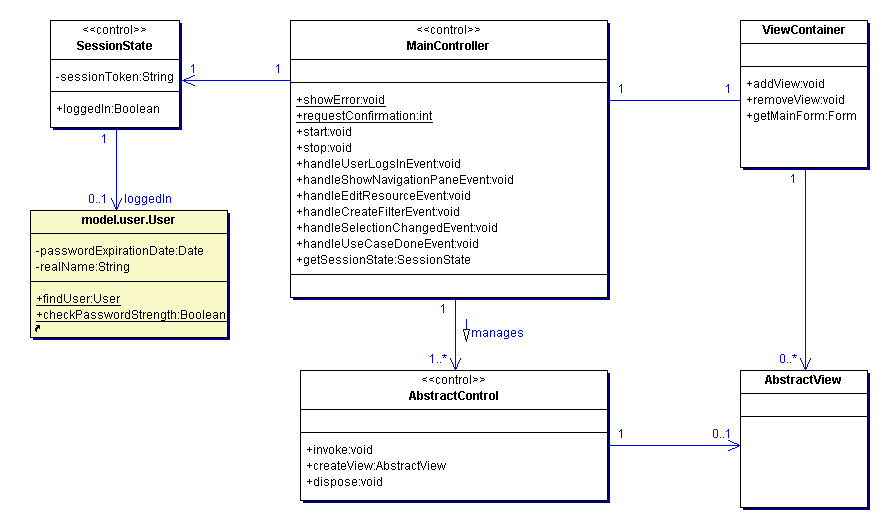
The following diagram depicts the main classes needed to realize an interaction between the user and the MRMS.
- Description
A SessionState describes a session of interaction between the MRMS and a user. A User is logged in in a SessionState if it references that User. If logged in it has a remote reference to an instance of MrmsFacade on the server which can be used by the control to communicate with the server.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
loggedIn(user: User): Boolean
- Effect
Checks whether the given User is logged in in this SessionState.
- Parameters
---
- Return
The boolean value true, if the given User is logged in in this SessionState.
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
MainController
- Description
The MainController manages concrete AbstractControls. It provides a ViewContainer were AbstractViews of AbstractControls may be plugged in. It is associated with a SessionState that provides a reference to the suitable MRMS server facade. Managed AbstractControls may interact with the MainController by using Events. For this the MainController provides delegate operations that may be registered at the AbstractControls. Moreover it contains static helper operations for showing dialogs to the user (used by AbstractControls). The MainController implements the Mediator pattern as described by the GoF. See also Section 3.7, “Sequence diagrams for package model.client”.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
static showError(text: String): void
- Effect
An error pop up is shown to the user.
- Parameters
text: Error message
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
AbstractControls
static requestConfirmation(text: String): int
- Effect
A confirmation dialog is shown to the user.
- Parameters
text: Confirmation message
- Return
An int value that is representing the decision of the user
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
AbstractControls
start(): void
- Effect
Activates default controls, MenuBar- and ToolBarControl, shows application window and starts event handling.
- Parameters
---
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
User
stop(): void
- Effect
Disposes the application and all its controllers.
- Parameters
---
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
MainController
handleUserLogsInEvent(sender: AbstractControl, args: System.Args): void
- Effect
A UserLogsInControl is created and invoked. Its view is plugged into the ViewContainer.
- Parameters
sender: The Sender of the event that invoked this operation
args: Arguments of the event that invoked this operation
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
AbstractControls using an EventHandle
showNavigationPaneEvent(sender: AbstractControl, args: System.Args): void
- Effect
An NavigationControl for the selected Resource is created and invoked. Its view is plugged into the ViewContainer.
- Parameters
sender: The Sender of the event that invoked this operation
args: Arguments of the event that invoked this operation
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
AbstractControls using an EventHandle
handleEditResourceEvent(sender: AbstractControl, args: System.Args): void
- Effect
An EditResourceControl for the selected Resource is created and invoked (uses static createEditResourceControl()) .
- Parameters
sender: The Sender of the event that invoked this operation
args: Arguments of the event that invoked this operation
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
AbstractControls using an EventHandle
handleCreateFilterEvent(sender: AbstractControl, args: System.Args): void
- Effect
A CreateFilterControl is created and invoked. Its view is plugged into the ViewContainer.
- Parameters
sender: The Sender of the event that invoked this operation
args: Arguments of the event that invoked this operation
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
AbstractControls using an EventHandle
handleUseCaseDoneEvent(sender: AbstractControl, args: System.Args): void
- Effect
The sender (concrete AbstractControl) is disposed and its view is removed from the ViewContainer.
- Parameters
sender: The Sender of the event that invoked this operation
args: Arguments of the event that invoked this operation
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
AbstractControls using an EventHandle
handleSelectionChangedEvent(sender: AbstractControl, args: System.Args): void
- Effect
All controls are informed about the new selection by an event.
- Parameters
sender: The Sender of the event that invoked this operation
args: Arguments of the event that invoked this operation
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
AbstractControls using an EventHandle
- DescriptionUser logs in
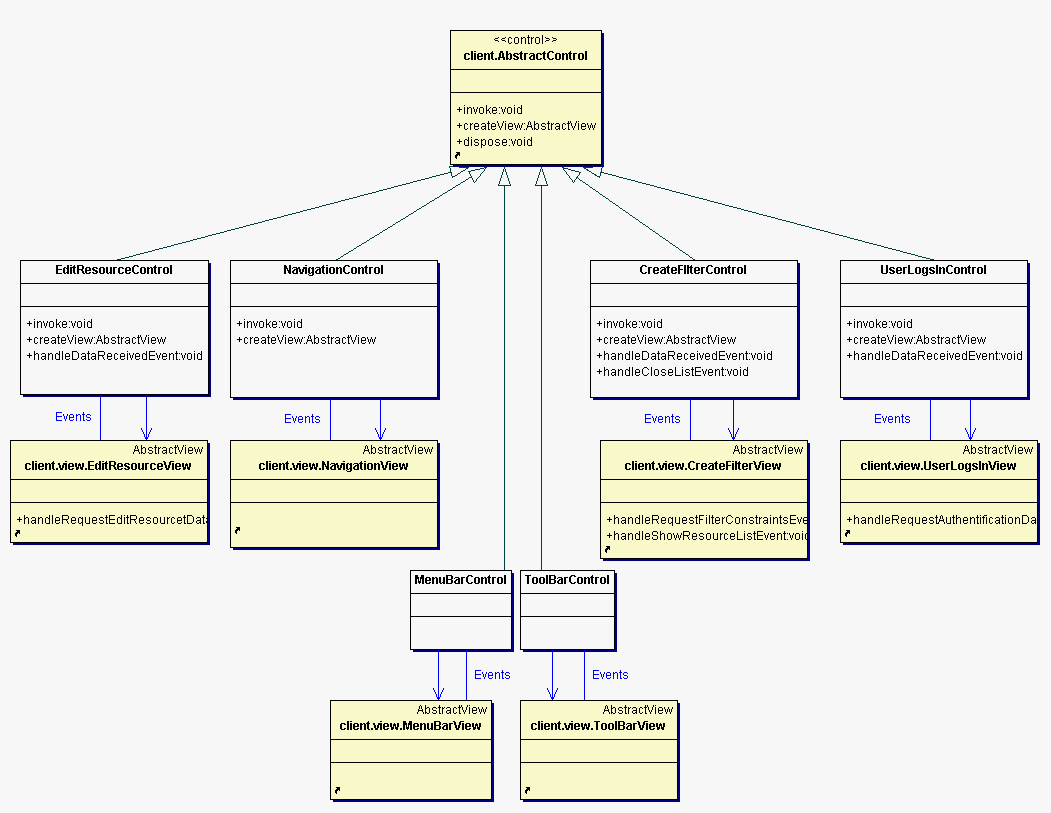
Base class for all concrete use case controllers. Encapsulates the common control flow. See also Section 3.7, “Sequence diagrams for package model.client”.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
invoke(): void
- Effect
Constructor operation that activates this AbstractControl instance.
- Parameters
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
MainController
createView(): AbstractView
- Effect
The AbstractControl is told to create its view component.
- Parameters
---
- Return
The created view component
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
MainController
dispose(): void
- Effect
Destroys the AbstractControl and its view component.
- Parameters
---
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
MainController
- Description
A ViewContainer is a component were the MainController may plug in AbstractViews of AbstractControls. See also Section 3.7, “Sequence diagrams for package model.client”.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
addView(view: AbstractView,location: int): void
- Effect
Adds the given AbstractView.
- Parameters
view: AbstractView to be added
location: An identifier determining the location to place the AbstractView
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
MainController
removeView(view: AbstractView): void
- Effect
Removes the given AbstractView.
- Parameters
view: AbstractView to be removed
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
MainController
- Description
A concrete AbstractControl for logging a user in. See also Section 3.7, “Sequence diagrams for package model.client”.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
invoke(sender: AbstractControl, args: System.Args): void
- Effect
The user is requested to enter his/her AuthentificationData.
- Parameters
sender: The Sender of the event that invoked this operation
args: Arguments of the event that invoked this operation
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
MainController
createView(): AbstractView
- Effect
An UserLogsInView is created and returned.
- Parameters
---
- Return
The created UserLogsInView
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
MainController
handleDataReceivedEvent(sender: AbstractControl, args: System.Args): void
- Effect
Either the user gets logged in or an error dialog is shown to him.
- Parameters
sender: The Sender of the event that invoked this operation
args: Arguments of the event that invoked this operation
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
UserLogsInView
- Description
A concrete AbstractControl for navigating entities managed by the MRMS system. See also Section 3.7, “Sequence diagrams for package model.client”.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
invoke(sender: AbstractControl, args: System.Args): void
- Effect
The NavigationControl waits for user's interaction.
- Parameters
sender: The Sender of the event that invoked this operation
args: Arguments of the event that invoked this operation
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
MainController
createView(): AbstractView
- Effect
An NavigationView is created and returned.
- Parameters
---
- Return
The created NavigationView
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
MainController
- Description
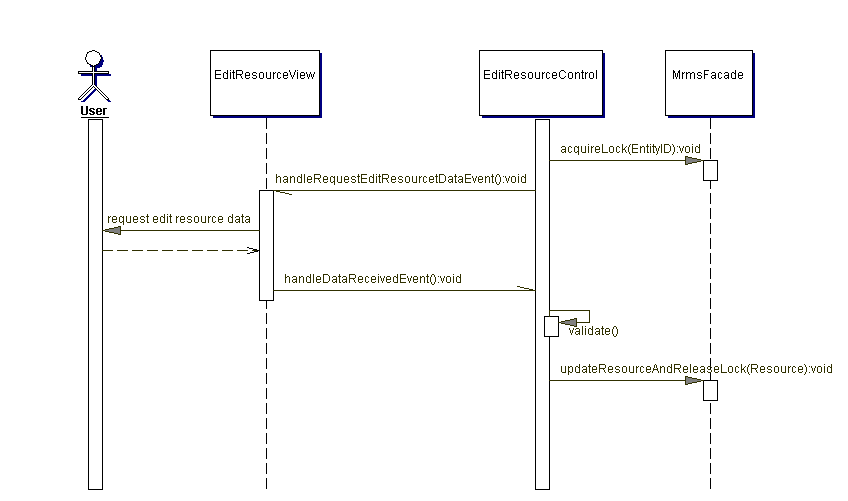
A concrete AbstractControl for editing Resources managed by the MRMS system. See also Section 3.7, “Sequence diagrams for package model.client”.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
invoke(sender: AbstractControl, args: System.Args): void
- Effect
Locks the Resource that shall be edited using the MrmsFacade. The user is requested to enter the changes to be performed.
- Parameters
sender: The Sender of the event that invoked this operation
args: Arguments of the event that invoked this operation
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
MainController
createView(): AbstractView
- Effect
An EditResourceView is created and returned.
- Parameters
---
- Return
The created EditResourceView
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
MainController
handleDataReceivedEvent(sender: AbstractControl, args: System.Args): void
- Effect
Updates the edited Resource using the MrmsFacade or shows an error dialog.
- Parameters
sender: The Sender of the event that invoked this operation
args: Arguments of the event that invoked this operation
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
EditResourceView
- Description
A concrete AbstractControl editing Resources managed by the MRMS system. See also Section 3.7, “Sequence diagrams for package model.client”.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
invoke(sender: AbstractControl, args: System.Args): void
- Effect
The user is requested to enter the filter constraints.
- Parameters
sender: The Sender of the event that invoked this operation
args: Arguments of the event that invoked this operation
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
MainController
createView(): AbstractView
- Effect
An CreateFilterView is created and returned.
- Parameters
---
- Return
The created CreateFilterView
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
MainController
handleDataReceivedEvent(sender: AbstractControl, args: System.Args): void
- Effect
Gets a list of matching resources and presents it to the user.
- Parameters
sender: The Sender of the event that invoked this operation
args: Arguments of the event that invoked this operation
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
CreateFilterView
handleCloseListEvent(sender: AbstractControl, args: System.Args): void
- Effect
Terminates the CreateFilterControl.
- Parameters
sender: The Sender of the event that invoked this operation
args: Arguments of the event that invoked this operation
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
CreateFilterView
- Description
A concrete AbstractControl that is managing an client's application window menu bar.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
invoke(sender: AbstractControl, args: System.Args): void
- Effect
---
- Parameters
sender: The Sender of the event that invoked this operation
args: Arguments of the event that invoked this operation
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
MainController
createView(): AbstractView
- Effect
An MenuBarView is created and returned.
- Parameters
---
- Return
The created MenuBarView
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
MainController
- Description
A concrete AbstractControl that is managing an client's application window tool bar.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
invoke(sender: AbstractControl, args: System.Args): void
- Effect
---
- Parameters
sender: The Sender of the event that invoked this operation
args: Arguments of the event that invoked this operation
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
MainController
createView(): AbstractView
- Effect
An ToolBarView is created and returned.
- Parameters
---
- Return
The created ToolBarView
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
MainController
- Description
A concrete AbstractView representing a log-in-dialog.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
handleRequestAuthentificationDataEvent(sender: AbstractControl, args: System.Args): void
- Description
A concrete AbstractView for navigating entities managed by the MRMS system.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
---
- Description
A concrete AbstractView for editing Resources managed by the MRMS system.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
handleRequestEditResourcetDataEvent(sender: AbstractControl, args: System.Args): void
- Description
A concrete AbstractView for creating a Filter.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
handleRequestFilterConstraintsEvent(sender: AbstractControl, args: System.Args): void
handleShowResourceListEvent(sender: AbstractControl, args: System.Args): void
- Description
A concrete AbstractView for that shows a menu bar.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
---
These diagrams verify the model.client package.
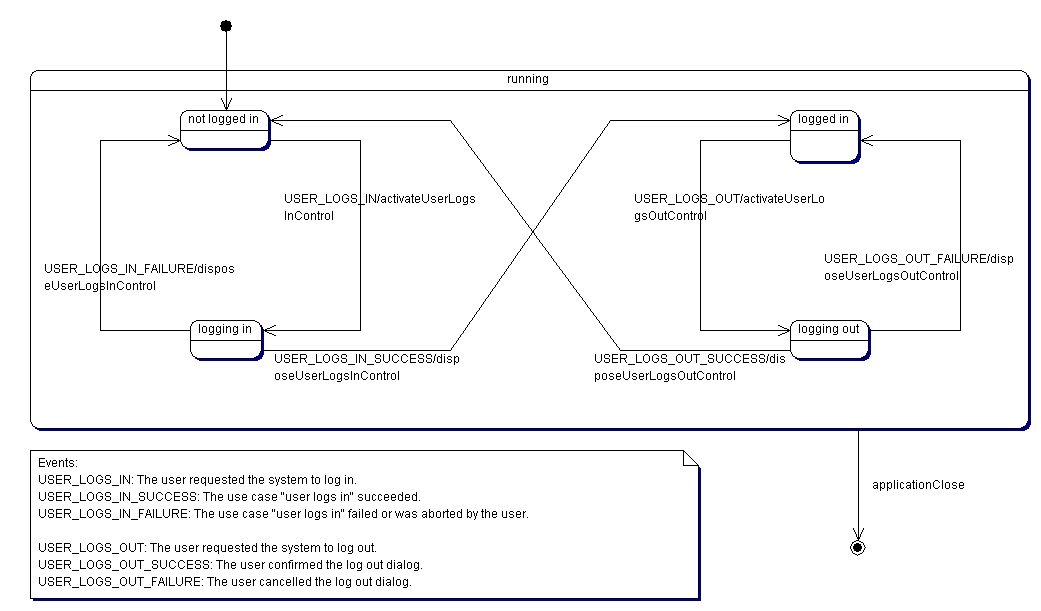
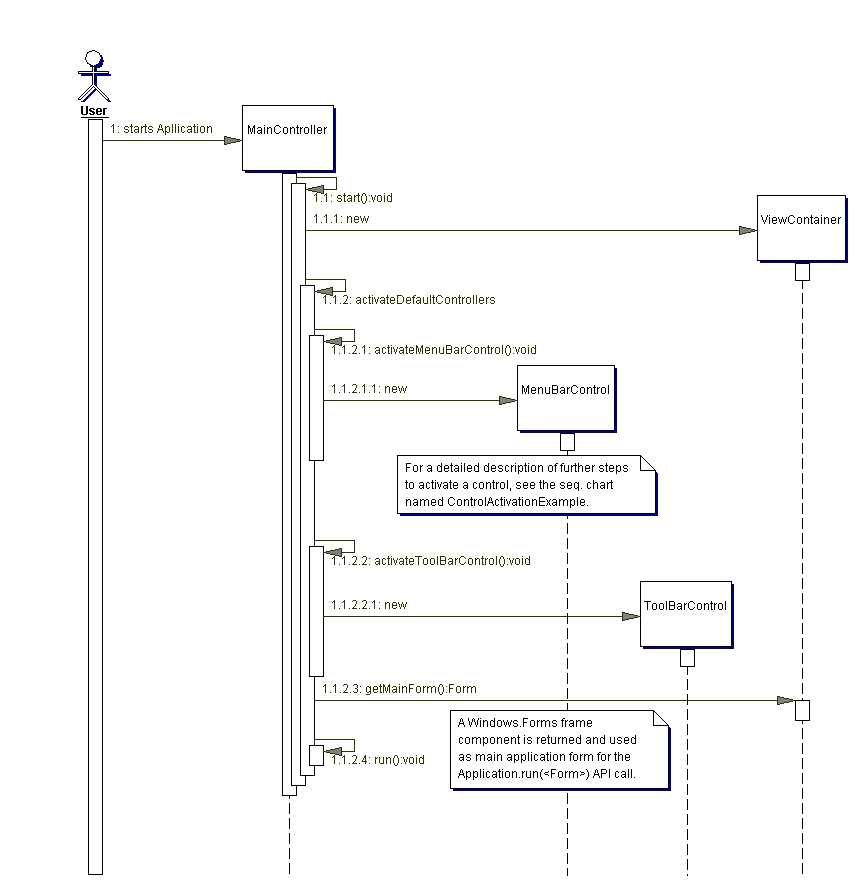
The following diagram illustrates the starting process of the application.
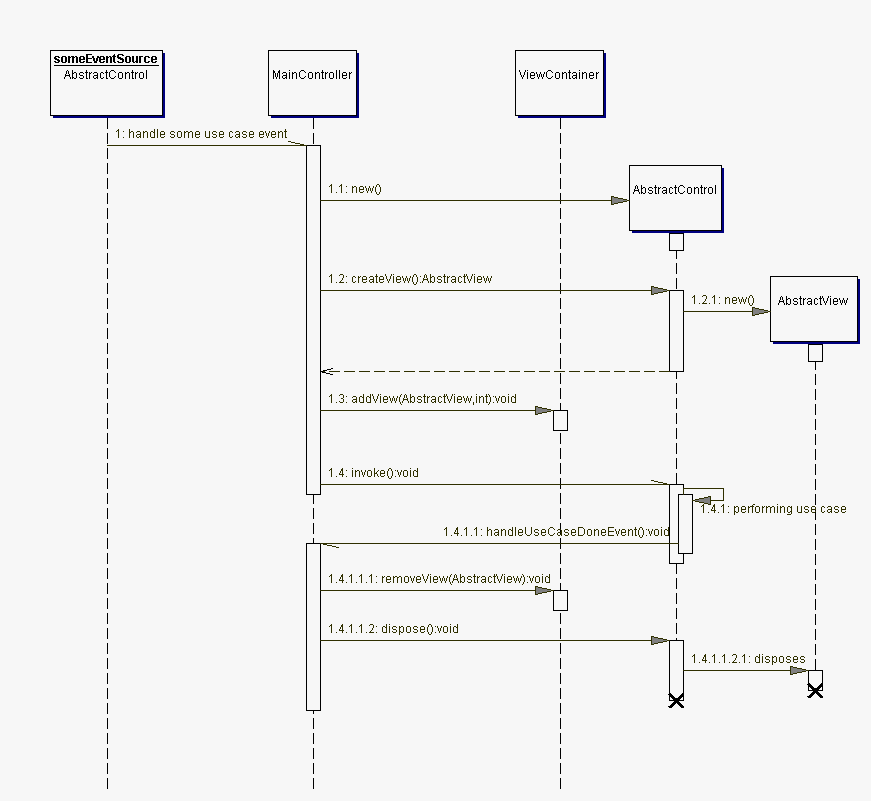
The following diagram illustrates the life cycle of an AbstractControl and its view.
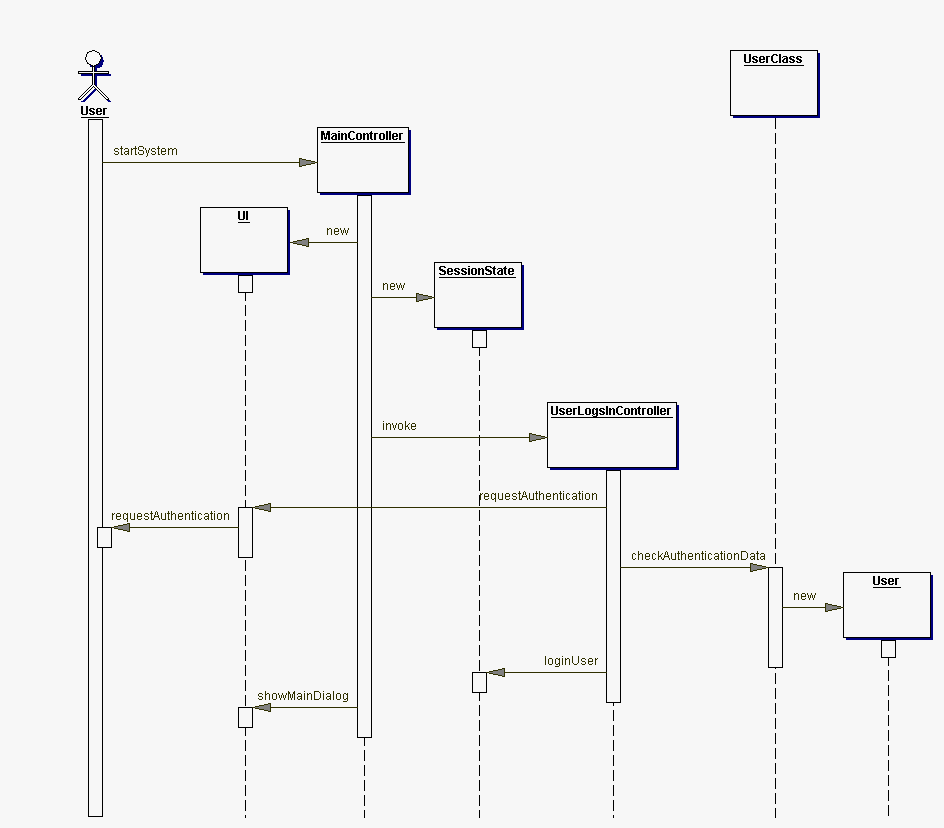
The following diagram illustrates the object interaction while performing the use case "User logs in"
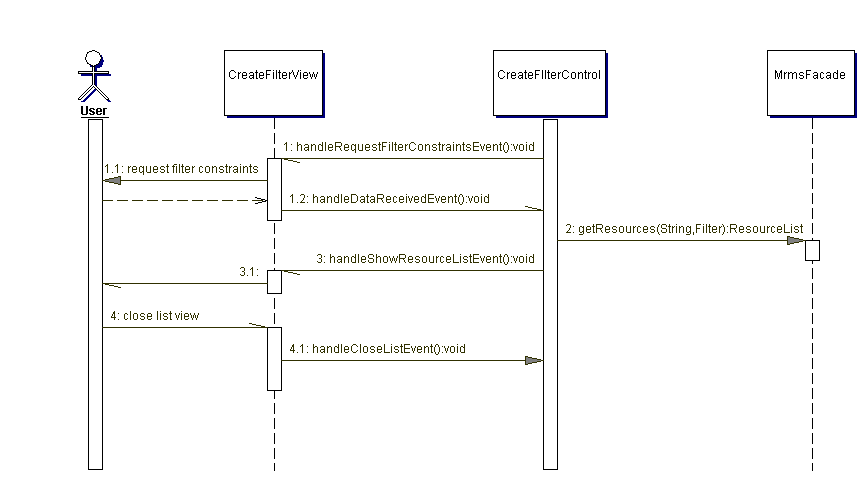
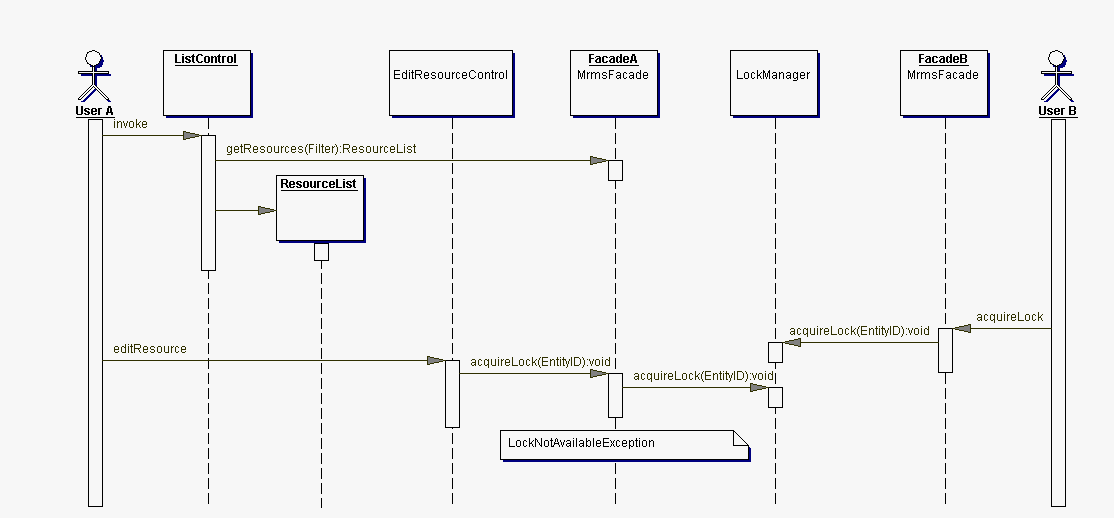
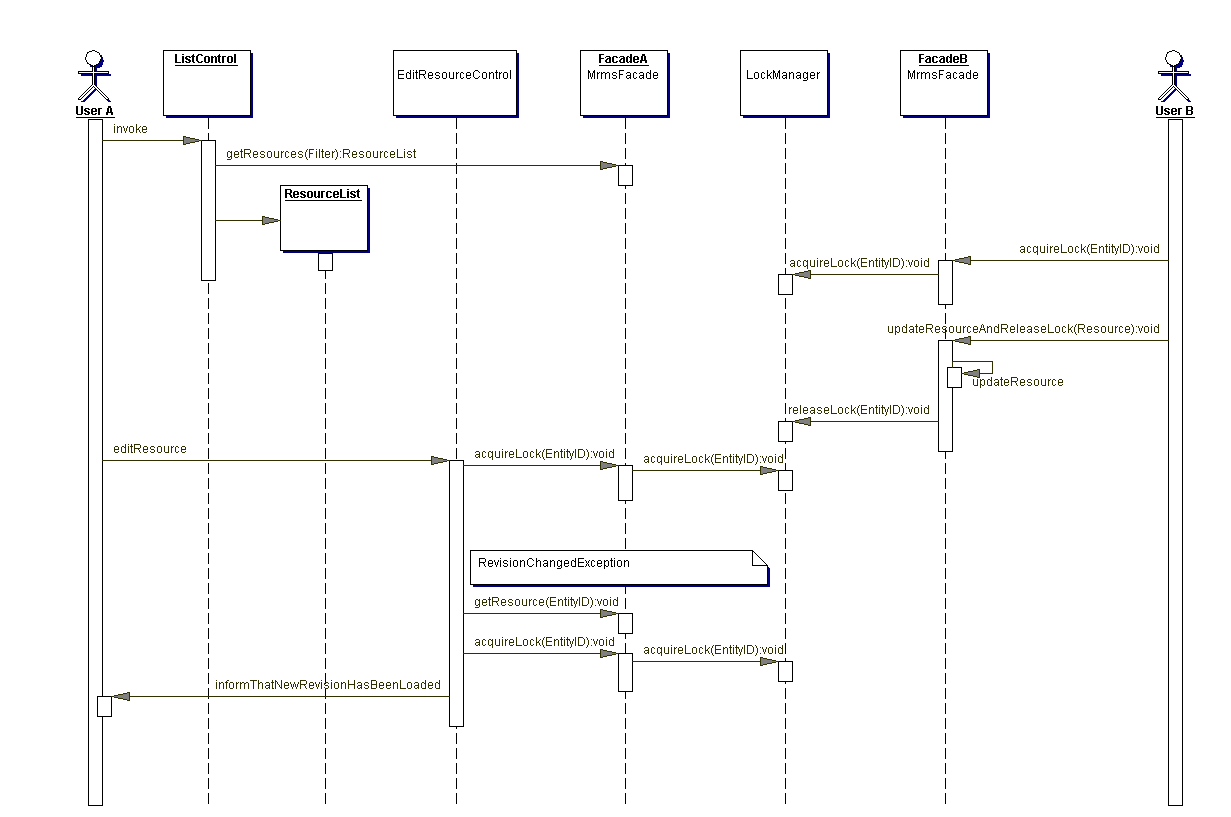
The following diagram illustrates the object interaction while performing the use case "Create filtered collection of resource entries"
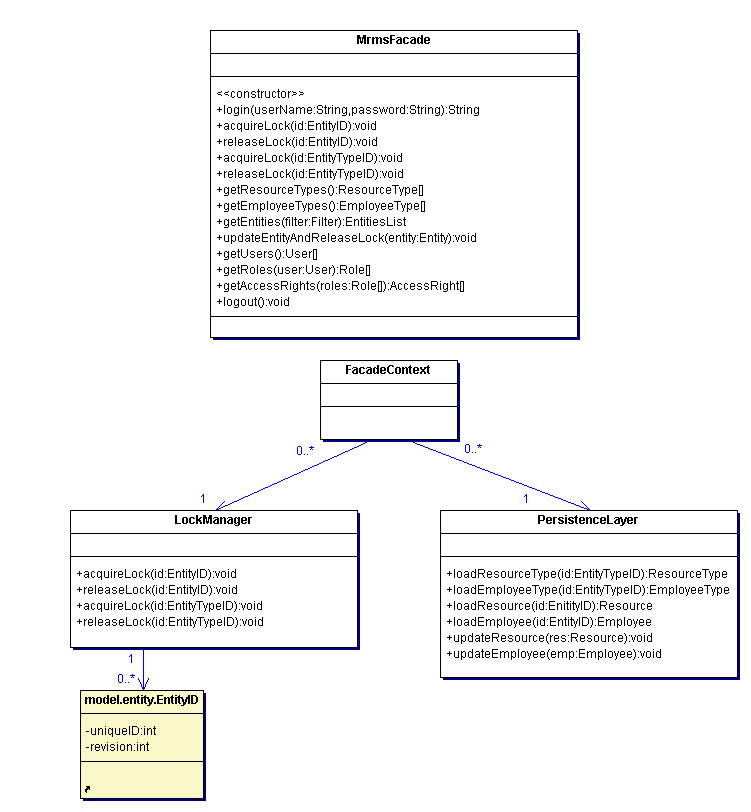
The client's interface to the server application is the MrmsFacade. Every instance of an MrmsFacade has a FacadeContext that provides access to a central LockManager as well as to the PersistenceLayer.
- Description
The MrmsFacade provides the server's functionality to connected clients. Every instance references one FacadeContext which provides access to a central LockManager as well as to the PersistenceLayer.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
login(user: User): MrmsFacade
- Effect
Constructor operation. Verifies and authorizes the given User and initializes a new MrmsFacade on success. If the User could not be authorized a LoginFailedException is thrown.
- Parameters
user (User): the User object identifying and authorizing the user to log in.
- Return
An instance of MrmsFacade
- Exceptions
LoginFailedException
- Actor
UserLogsInControl
acquireLock(id:EntityID): void
- Effect
Requests to acquire a lock for the given EntityID at the central LockManager instance.
- Parameters
id (EntityID): the EntityID of the Entity that should be locked.
- Return
---
- Exceptions
LockNotAvailableException - if the id is already locked
RevisionChangedException - if the id's revision is not current
- Actor
EditResourceControl
releaseLock(id: EntityID): void
- Effect
Requests to release a lock for the given EntityID at the central LockManager instance.
- Parameters
id (EntityID): the EntityID of the Entity to unlock
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
EditResourceControl
acquireLock(id:EntityTypeID): void
- Effect
Requests to acquire a lock for the given EntityTypeID at the central LockManager instance.
- Parameters
id (EntityTypeID): the EntityTypeID of the EntityType that should be locked.
- Return
---
- Exceptions
LockNotAvailableException - if the id is already locked
RevisionChangedException - if the id's revision is not current
- Actor
EditResourceControl
releaseLock(id: EntityTypeID): void
- Effect
Requests to release a lock for the given EntityTypeID at the central LockManager instance.
- Parameters
id (EntityTypeID): the EntityTypeID of the EntityType to unlock
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
EditResourceControl
getResourceTypes(): ResourceType[]
- Effect
Getter without side effects.
- Parameters
---
- Return
An array with all ResourceTypes that the administrator has configured in the system.
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
NavigationControl
getEmployeeTypes(): EmployeeType[]
- Effect
Getter without side effects.
- Parameters
---
- Return
An array with all EmployeeTypes that the administrator has configured in the system.
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
NavigationControl
getEntities(filter: Filter): EntitiesList
- Effect
Requests a list of Entitys matching the given Filter; has no side effects.
- Parameters
filter (Filter): the Filter that all returned entities must match.
- Return
an EntitiesList containing all matching Entities
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
All controls that need to access entities.
updateEntityAndReleaseLock(entity: Entity): void
- Effect
Updates the given Entity object and releases the associated lock.
- Parameters
entity (Entity): the Entity to update
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
EditEntityControl
getUsers(): User[]
- Effect
Getter without side effects.
- Parameters
---
- Return
An array with all Users that the administrator has configured in the system.
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
NavigationControl
getRoles(user: User): Role[]
- Effect
Getter without side effects.
- Parameters
user (User): the user whose roles should be returned
- Return
An array with all Roless that the administrator has configured in the system for a specifc user.
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
NavigationControl and EditUserControl
getAccessRights(roles: Role[]): AccessRight[]
- Effect
Getter without side effects.
- Parameters
roles (Role[]): the roles whose access rights should be returned
- Return
An array with merged AccessRights that all given Roles have.
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
NavigationControl and EditUserControl
logout(): void
- Effect
Informs the MrmsFacade that the client does not need its services anymore; any open locks will be released.
This method is automatically called if the client did not do any request for a specific amount of time (15 Min).
- Parameters
---
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
MainController
- Description
The FacadeContext provides a context for a MrmsFacade which consists of references to the central instances of LockManager and PersistenceLayer.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
---
- Description
The LockManager holds information about locked Entitys and EntityTypes. Client classes may acquire and release locks with instances of this class.
- Attributes
---
- Operations
acquireLock(id:EntityID): void
- Effect
Requests to acquire a lock for the given EntityID at the central LockManager instance.
- Parameters
id (EntityID): the EntityID of the Entity that should be locked.
- Return
---
- Exceptions
LockNotAvailableException - if the id is already locked
RevisionChangedException - if the id's revision is not current
- Actor
EditResourceControl
releaseLock(id: EntityID): void
- Effect
Requests to release a lock for the given EntityID at the central LockManager instance.
- Parameters
id (EntityID): the EntityID of the Entity to unlock
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
EditResourceControl
acquireLock(id:EntityTypeID): void
- Effect
Requests to acquire a lock for the given EntityTypeID at the central LockManager instance. A lock on an EntityType also locks all Entitys of this type and no Entitys of this type may be created.
- Parameters
id (EntityTypeID): the EntityTypeID of the EntityType that should be locked.
- Return
---
- Exceptions
LockNotAvailableException - if the id is already locked
RevisionChangedException - if the id's revision is not current
- Actor
EditResourceControl
releaseLock(id: EntityTypeID): void
- Effect
Requests to release a lock for the given EntityTypeID at the central LockManager instance.
- Parameters
id (EntityTypeID): the EntityTypeID of the EntityType to unlock
- Return
---
- Exceptions
---
- Actor
EditResourceControl
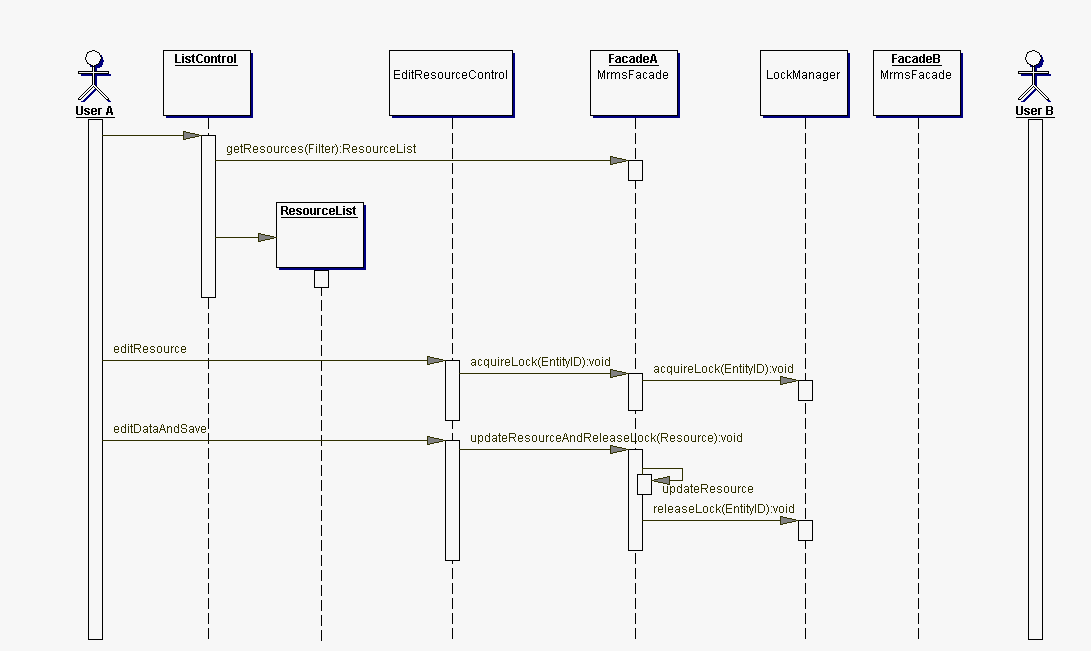
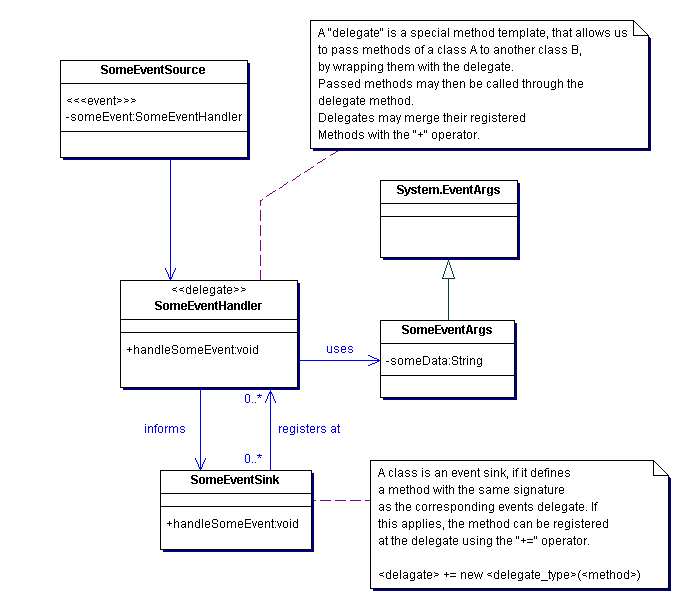
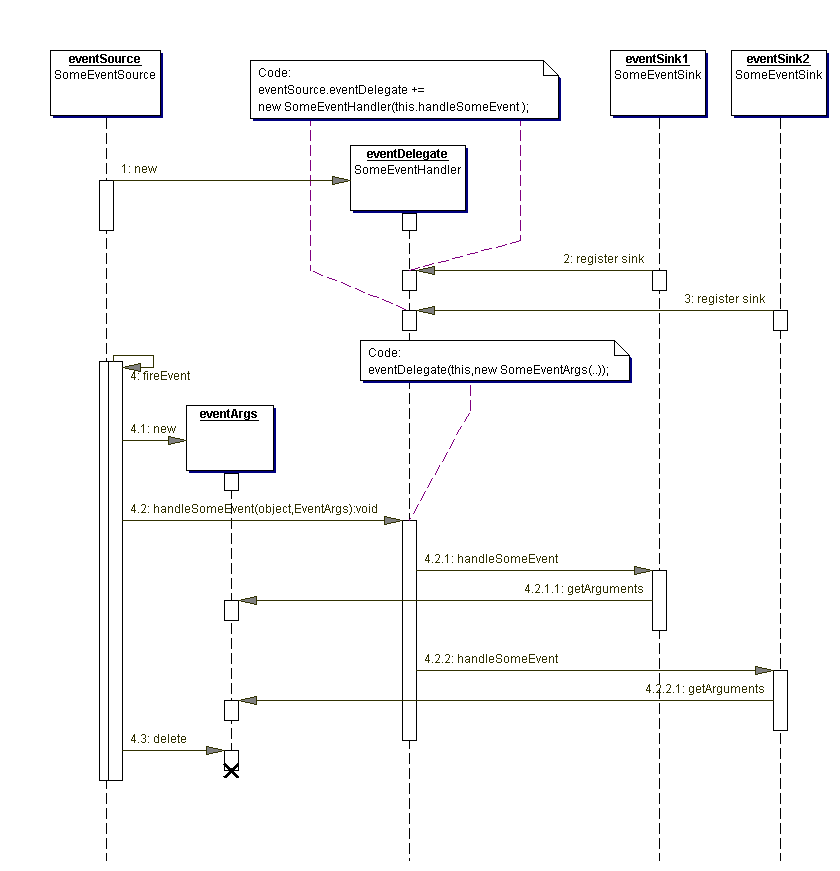
The MRMS is implemented for the .NET platform and therefore partly builds up on the .NET model for event handling. The following two figures are an overview on how that mechanism works.
These are the use cases derived from the additional functionality “Resource Reservation”.
- Goal
A new reservation for a resource is created.
- Category
Primary
- External Actors
User
- Precondition
A user is logged in who has proper access rights to create the new resource reservation.
- Triggering Event
The user requests the system to create a new resource reservation.
- Postcondition Success
A new resource reservation has been created according to the users input.
- Postcondition Failure
No new resource reservation has been created.
- Description
The system requests the user to choose the resource, start time, end time of the reservation and the customer.
The user determines resource reservation and submits his input.
The system creates a new resource reservation.
- Extensions
---
- Alternatives
---
- Additional Requirements
---
- Annotation
---
- Goal
The reservation for a resource is deleted.
- Category
Primary
- External Actors
User
- Precondition
A user is logged in who has proper access rights to delete the resource reservation.
- Triggering Event
The user requests the system to delete a resource reservation.
- Postcondition Success
The resource reservation has been deleted.
- Postcondition Failure
The resource reservation has not been deleted.
- Description
The system requests the user to choose a resource reservation.
The user determines the resource reservation to delete and submits his input.
The system deletes the resource reservation.
- Extensions
---
- Alternatives
---
- Additional Requirements
---
- Annotation
---
- Goal
The reservation for a resource is changed.
- Category
Secondary
- External Actors
User
- Precondition
A user is logged in.
- Triggering Event
The user requests the system to create a filtered collection of resource reservations.
- Postcondition Success
The user is shown a collection of resource reservations that passed the filter he created.
- Postcondition Failure
---
- Description
The system requests the user to choose a resource reservation for changing.
The user determines the resource reservation to change and submits his input.
The system changes the resource reservation.
- Extensions
---
- Alternatives
---
- Additional Requirements
---
- Annotation
---
- Goal
Collect a set of resources reservations meeting a specific criterion and offer it to the user for further processing.
- Category
Secondary
- External Actors
User
- Precondition
A user is logged in who has proper access rights to change the resource reservation.
- Triggering Event
The user requests the system to change a resource reservation.
- Postcondition Success
The resource reservation has been changed.
- Postcondition Failure
The resource reservation has not been changed.
- Description
The system requests the user to configure a filter listed resource reservations will have to pass
The system collects all resource reservations passing the specified filter and offers them to the user for further processing.
- Extensions
---
- Alternatives
---
- Additional Requirements
---
- Annotation
---